根据CPU温度控制风扇
2021年9月13日...大约 3 分钟
目的
使用三极管当作开关,根据CPU的温度,通过树莓派的GPIO控制风扇是否开启
1.准备
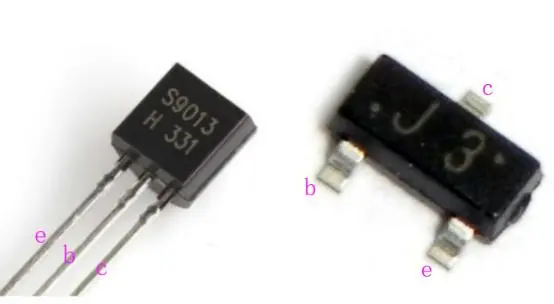
- 三极管一个,我用的三极管型号为S9013
- 1k电阻一个
- 电线若干
- 热缩管若干
2.接线
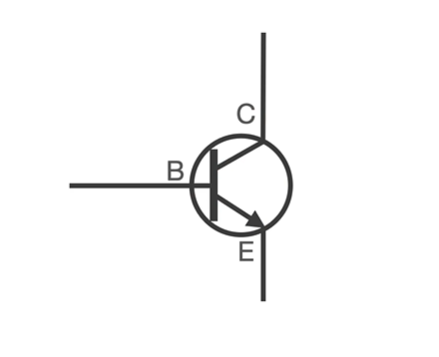
三极管工作原理
三极管有三个引脚,分别为基极(B)、集电极(C)、发射极(E)。只需要给基极(B)轻微的电流,集电极(C)和发射极(E)就能导通,以此充当开关的作用
如图所示
S9013 针脚
通过树莓派GPIO针脚图,我们需要做的是,将基极接到树莓派的GPIO口上(我是用11号针脚,也就是GPIO 17),发射极接地(6号针脚),集电极接风扇负极出来的那根线。风扇正极接4号针脚(也就是5V供电)
大概就是这样吧,中间有个 1K电阻
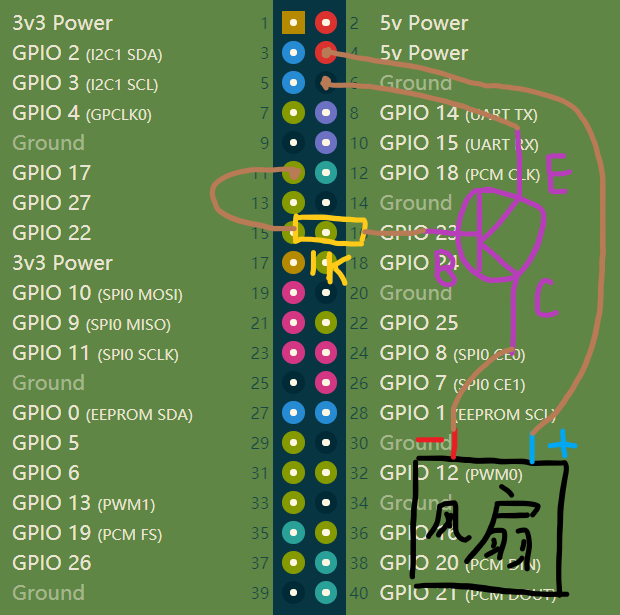
3.编写程序
参考了https://lsun.net/posts/raspberry-pi-auto-fan/这篇文章的代码,我自己添加了 日志输出 和 针对systemd service开机自启 的一些修改
auto_fan.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import signal
import time
import logging
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from time import sleep
# 日志配置
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, #控制台打印的日志级别
filename=r'/home/ubuntu/shellscript/auto_fan_log/' + time.strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S", time.localtime()) + r'.txt',
filemode='a', ##模式,有w和a,w就是写模式,每次都会重新写日志,覆盖之前的日志
#a是追加模式,默认如果不写的话,就是追加模式
format='%(asctime)s - %(pathname)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s' #日志格式
)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # 使用BCM引脚模式
channel = 17 # 使用BCM17(对应物理引脚号11)接口控制开关
start_temp = 45 # 启动风扇的温度阈值(℃)
end_temp = 37 # 关闭风扇的温度阈值(℃)
# GPIO.setup(channel, GPIO.OUT, initial = GPIO.LOW) # 初始化控制引脚
GPIO.setup(channel, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(channel, GPIO.LOW)
is_high = GPIO.LOW # 用于标记风扇是否打开 避免频繁调用output
# 使用"systemctl stop 命令时,传入SIGTERM 信号,退出脚本并重置引脚"
def terminateProcess(signalNumber, frame):
logging.info('(SIGTERM) terminating the process')
GPIO.cleanup(channel) # 重置引脚
logging.info('--stop script--')
sys.exit()
logging.info('--start script--')
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, terminateProcess)
try:
while True:
# 获取当前SoC温度
temp = open('/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp')
temp = int(temp.read()) / 1000
if temp > start_temp and not is_high: # 当SoC温度超过启动阈值且风扇处于关闭状态
GPIO.output(channel, GPIO.HIGH) # 打开风扇
print("--Turn on the fan--")
logging.info('Turn on the fan')
is_high = GPIO.HIGH # 标记风扇状态为打开
elif temp < end_temp and is_high: # 当SoC温度低于关闭阈值且风扇处于打开状态
GPIO.output(channel, GPIO.LOW) # 关闭风扇
print("--Turn off the fan--")
logging.info('Turn off the fan')
is_high = GPIO.LOW # 标记风扇状态为关闭
sleep(10) # 每隔10秒监控一次
except:
pass
# 重置该引脚
# GPIO.cleanup(channel)
# logging.info('--stop--')4.开机自启
在/etc/systemd/system/中新建一个<名字>.service文件
[Unit]
Description=<服务名称>
[Service]
Type=simple
User=<运行用户>
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 <python脚本的绝对路径>
KillMode=mixed
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target其中的KillMode=mixed表示:当执行systemctl stop命令时,主进程将收到 SIGTERM 信号,子进程收到 SIGKILL 信号
在上面的代码中,使用 python 的 signalk 库来接收处理 SIGTERM 信号
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, terminateProcess)当接收到 SIGTERM 信号时,会执行这里面的函数。这样才能完整的结束python脚本并重置引脚
def terminateProcess(signalNumber, frame):
logging.info('(SIGTERM) terminating the process')
GPIO.cleanup(channel) # 重置引脚
logging.info('--stop script--')
sys.exit()最后执行
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl enable rclone以后开机就能自动启动脚本了
